
Chronic disease is the term used when course of the illness lasts for more than three months. Chronic diseases that are most common include the following. Many chronic diseases have genetic components which increases disease risk in certain people. Environment and exposure to polluted air, lifestyle choices including diet and smoking may affect the outcome of chronic disease.
Chronic diseases that are most common, include the following.
Arthritis is defined as painful swelling one or more joints. Main symptom is pain and stiffness. Most common arthritis are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Current treatment recommendation is nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, NSAIDs reduce both pain and inflammation ibuprofen or naproxen may help as well. Other treatments are to lose weight, increase activity and exercise that is low impact such as water aerobics or swimming and use of hot and cold therapy.Turmeric intake reduces pain and inflammation of the joints. Massage therapy is also helpful. If you suffer from joint pain please add to the survey. This would help in finding out prevailing of arthritis in our community and may help to find better diagnoses and treatment. Of course personal identity will not be revealed or compromised. Survey to include name, age, gender, city, symptoms of pain, swelling, limitation of joint movements, duration of symptoms, treatment used such as Advil naproxen , steroids, surgery.
Asthma is a chronic disease involving the airways such as bronchial tubes in the lungs.
In asthma these tubes get inflamed. This makes it difficult for air to move in and out of the lungs, causing symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath and/or chest tightness. Occurrence of these symptoms is closely related to physical activity. And, some otherwise healthy people can develop asthma symptoms only when exercising.This is called exercise-induced bronchoconstriction (EIB), or exercise-induced asthma (EIA).
People with a family history of allergies or asthma are more prone to developing asthma. Many people with asthma also have allergies. This is called allergic asthma.
Occupational asthma is caused by inhaling fumes, gases, dust or other potentially harmful substances while on the job.
Childhood asthma impacts millions of children and their families. In fact, the majority of children who develop asthma do so before the age of five.
There is no cure for asthma, but once it is properly diagnosed and a treatment plan is in place you will be able to manage your condition, and your quality of life will improve.
An allergist / immunologist is the best qualified physician in diagnosing and treating asthma. With the help of your allergist, you can take control of your condition and participate in normal activities.
A biologic is a medication made from the cells of a living organism, such as bacteria or mice, which is then modified to target specific molecules in humans. For asthma, the targets are antibodies, inflammatory molecules, or cell receptors. By targeting these molecules, biologics work to disrupt the pathways that lead to inflammation that causes asthma symptoms.
Currently there are five approved biologics for asthma – Omalizumab, Mepolizumab, Reslizumab, Benralizumab, and Dupilumab Treatment is given by injection for a period of four months.
Other treatment includes change in the environments, stop smoking, avoiding dust or pollens, Use of Bronchodilators as inhalation therapy and Steroids for short-term use.
If you suspect you’re having a heart attack, immediately call your local emergency number. If you don’t have access to emergency medical services, have someone drive you to the nearest hospital. Drive yourself only as a last resort.
If you have risk factors for coronary artery disease — such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, tobacco use, diabetes, a strong family history of heart disease or obesity — talk to your doctor. He or she may want to test you for the condition, especially if you have signs or symptoms of narrowed arteries.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is an umbrella term used to describe progressive lung diseases including emphysema, chronic bronchitis, and refractory (non-reversible) asthma. This disease is characterized by increasing breathlessness. COPD may be mild, Moderate or Severe.
Treatments include many different drugs, special exercises, oxygen therapy, surgery, and complementary therapies.
Medications for COPD can help improve your lung capacity, ease inflammation, relax muscles in your airways, and improve your breathing. They include:
Bronchodilators that you breathe in through an inhaler. These come in short- and long-acting forms. Some stop the muscles in your airways from tightening up (anticholinergics). Others relax muscles that are already tight (beta agonists).
Anti-inflammatory meds or corticosteroids (or steroids) are often inhaled COPD drugs. But if your symptoms are getting worse, you may take pills for a short time.
Antibiotics to fight infections that cause symptom flare-ups.
Vaccinations against the flu or pneumonia.
Roflumilast (Daliresp). It’s the first of a new class of COPD drugs called phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors that ease flares for people at the severe stage.
Cystic Fibrosis is an inherited disorder that causes severe damage to the lungs, digestive system and other organs in the body.
Cystic fibrosis affects the cells that produce mucus, sweat and digestive juices.
Symptoms vary and can include
Treatments may ease symptoms and reduce complications.
Newborn screening helps with early diagnosis.
Genetic (or carrier) testing not only plays a key role in the diagnosis of cystic fibrosis, but testing also allows parents to find out what their chances of having a child with CF are to help inform important family planning decisions. A person may wish to get a genetic carrier test for CF or a sweat test if they have symptoms of CF, based on their doctor’s recommendations.
Cardiovascular disease includes conditions that affect the structures or function of your heart, such as:
Coronary artery disease develops when the major blood vessels that supply your heart with blood, oxygen and nutrients (coronary arteries) become damaged or diseased. Cholesterol-containing deposits (plaque) in your arteries and inflammation are usually to blame for coronary artery disease.
When plaque builds up, it narrows your coronary arteries, decreasing blood flow to your heart. Eventually, the decreased blood flow may cause chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, or other coronary artery disease signs and symptoms. A complete blockage can cause a heart attack.
Because coronary artery disease often develops over decades, you might not notice a problem until you have a significant blockage or a heart attack. But there’s plenty you can do to prevent and treat coronary artery disease. A healthy lifestyle can make a big impact.
If your coronary arteries narrow, they can’t supply enough oxygen-rich blood to your heart — especially when it’s beating hard, such as during exercise. At first, the decreased blood flow may not cause any coronary artery disease symptoms. As plaque continues to build up in your coronary arteries, however, you may develop coronary artery disease signs and symptoms, including:
The pain usually goes away within minutes after stopping the stressful activity. In some people, especially women, this pain may be fleeting or sharp and felt in the neck, arm or back.
Women are somewhat more likely than men are to experience less typical signs and symptoms of a heart attack, such as neck or jaw pain. Sometimes a heart attack occurs without any apparent signs or symptoms.
Moderate Alzheimer’s is typically the longest stage and can last for many years. As the disease progresses, the person with Alzheimer’s will require a greater level of care.
Medications and therapies may help manage symptoms. Some causes are reversible.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved two types of medications — cholinesterase inhibitors (Aricept, Exelon, Razadyne) and memantine (Namenda) — to treat the cognitive symptoms (memory loss, confusion, and problems with thinking and reasoning) of Alzheimer’s disease.
As Alzheimer’s progresses, brain cells die and connections among cells are lost, causing cognitive symptoms to worsen. While current medications cannot stop the damage Alzheimer’s causes to brain cells, they may help lessen or stabilize symptoms for a limited time by affecting certain chemicals involved in carrying messages among the brain’s nerve cells. Doctors sometimes prescribe both types of medications together.
Three cholinesterase inhibitors are commonly prescribed:
Relaxes blood vessels, lowers blood pressure and prevents diabetes-related kidney damage.
Lisinopril can reduce high blood pressure and treat heart failure. It can reduce the risk of death after a heart attack and Benazepril can reduce high blood pressure.
Slows heart rate and decreases blood pressure. When taken in eye-drop form, it reduces eye pressure.
Atenolol is used with or without other medications to treat high blood pressure (hypertension). … This medication is also used to treat chest pain (angina) and to improve survival after a heart attack.Metoprolol is a beta-blocker that affects the heart and circulation (blood flow through arteries and veins). Metoprolol is used to treat angina (chest pain) and hypertension (high blood pressure). Metoprolol is also used to lower your risk of death
Nifedipine and Irbesartan can reduce blood pressure, reduce chest pain. Later can treat diabetic nephropathy
Relaxes blood vessels.
Amlodipine and Nifedipine can treat high blood pressure and angina
Vasodilator
Widens blood vessels.
Hydralazine can treat high blood pressure.
Warning Signs of Stroke
Ischemic Stroke (Clots) Occurs when a blood vessel supplying blood to the brain is obstructed.
Hemorrhagic Stroke (Bleeds) Occurs when a weakened blood vessel ruptures. Hemorrhagic stroke
Hemorrhagic strokes are caused by blood leaking into the brain, so treatment focuses on controlling the bleeding and reducing the pressure on the brain.
Treatment can begin with drugs given to reduce the pressure in the brain, control overall blood pressure, prevent seizures and prevent sudden constrictions of blood vessels.
If an individual is taking blood-thinning anticoagulants or an antiplatelet medication like warfarin or clopidogrel, they can be given drugs to counter the effects of the medication or blood transfusions to make up for blood loss.
Surgery can be used to repair any problems with blood vessels that have led or could lead to hemorrhagic strokes. Surgeons can place small clamps at the base of aneurysms or fill them with detachable coils to stop blood flow and prevent rupture.
If the hemorrhage is caused by arteriovenous malformations (AVMs), surgery can also be used to remove them if they are not too big and not too deep in the brain. AVMs are tangled connections between arteries and veins that are weaker and burst more easily than other normal blood vessels.
TIA (Transient Ischemic Attack) Called a “mini stroke,” it’s caused by a serious temporary clot. …
Cryptogenic stroke (CS) is defined as cerebral ischemia of obscure or unknown origin. The cause of CS remains undetermined because the event is transitory or reversible, investigations did not look for all possible causes, or because some causes truly remain unknown. One third of the ischemic strokes is cryptogenic.
Use FAST to remember and recognize the following signs and symptoms of stroke:
The Best Foods to Prevent Stroke
Ischemic strokes are most often caused by atherosclerosis, or hardening of the arteries, and carry the same risk factors as heart attacks (myocardial infarction, coronary artery disease) and peripheral vascular disease. These include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, and smoking.
Aspirin prevents blood clots from forming in the arteries. It can help certain people lower their risk of a heart attack or stroke. But taking aspirin isn’t right for everyone, because it can cause serious bleeding. You and your doctor can decide if aspirin is a good choice for you.
Strokes are life-changing events that can affect a person both physically and emotionally. After a stroke, successful recovery will often involve specific therapies and support, such as:
Speech therapy: This helps with any problems producing or understanding speech. Practice, relaxation, and changing communication style can all help.
Physical therapy: This can help a person relearn movement and co-ordination. It is important to stay active, even if it is difficult at first.
Occupational therapy: This is used to help a person to improve their ability to carry out routine daily activities, such as bathing, cooking, dressing, eating, reading, and writing.
Support groups: These help with common mental health problems such as depression that can occur after a stroke. Many find it useful to share common experiences and exchange information.
Support from friends and family: The people closest to a person should offer practical support and comfort after a stroke. Letting friends and family know what can be done to help is very important.
Rehabilitation is an important and ongoing part of treatment. With the right assistance and the support of loved ones, rehabilitation to a normal quality of life is possible, depending on the severity of the stroke.
The best way to prevent a stroke is to address the underlying causes. This is best achieved through lifestyle changes, including:
Please submit this form if anyone in your family had cancer
Diabetes is a disease in which blood sugar levels are too high. Glucose comes from the foods we eat. Insulin is a hormone that helps the glucose gets into cells to give energy.
Diabetes Type 1: Pancreas does not make insulin.
Diabetes Type 2: A chronic condition that affects the way the body processes blood sugar (glucose).
Prediabetes is a serious health condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal, but not high enough yet to be diagnosed as type 2 diabetes. … Of those with prediabetes, 90% don’t know they have it. Prediabetes puts you at increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and stroke.
A fasting blood sugar level from 100 to 125 mg/dL (5.6 to 7.0 mmol/L) is considered prediabetes. This result is sometimes called impaired fasting glucose. A fasting blood sugar level of 126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L) or higher indicates type 2 diabetes.
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that is first seen in a pregnant woman who did not have diabetes before she was pregnant. Some women have more than one pregnancy affected by gestational diabetes. Gestational diabetes usually shows up in the middle of pregnancy.
Doctors most often test for it between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy.
Gestational diabetes me lead to problems in pregnancy including large size baby causing difficulty in birth and resulting in C-section delivery of the baby.
It may result in high blood pressure with proteins in the urine and swelling of fingers and toes resulting in pre-eclampsia. That results in higher maternal and fetal mortality. It may also cause low blood sugars
With the gestational diabetes woman should eat healthy foods and see a dietitian.
Exercise regularly at least 30 minutes of moderate intensity physical activity at least five days a week.
Monitor blood sugars regularly take insulin if necessary.
Common warnings signs of diabetes include:
Prevention
Boost your intake of vegetables and fresh fruit
Eat more low-fat dairy products and beans
Choose whole grains diet
Eat fish, poultry, and lean meat instead of fatty red meat or processed meat
Diabetes: Education and Support
Diabetes Self-Management Education and Support (DSMES) services help people with diabetes learn how to take the best care of themselves. Ask us or your doctor for a referral to DSMES services to help you manage your diabetes.
How will DSMES help me?
When you learn that you have diabetes, your first question might be, “What can I eat?” DSMES will answer this question and many others. We will teach you how to stay healthy and how to manage your diabetes.
DSMES services will help you:
Epilepsy and Seizures: A seizure is a single occurrence, whereas epilepsy is a neurological condition characterized by two or more unprovoked seizures.
seizure triggers. Triggers are situations that can bring on a seizure in some people with epilepsy. Some people’s seizures are brought on by certain situations. Triggers can differ from person to person, but common triggers include tiredness and lack of sleep, stress, alcohol, and not taking medication. Seizures are not always related to epilepsy. They can be a symptom of a disruption of brain function, such as from a high fever, a head injury or lack of oxygen.
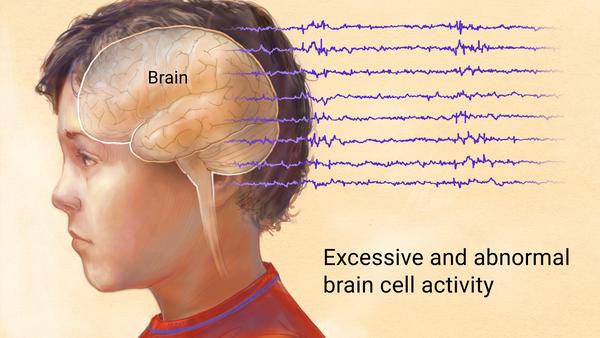
Epilepsy may occur as a result of a genetic disorder or an acquired brain injury, such as a trauma or stroke. During a seizure, a person experiences abnormal behavior, symptoms, and sensations, sometimes including loss of consciousness. There are few symptoms between seizures. Epilepsy is usually treated by medications and in some cases by surgery, devices, or dietary changes.
Obesity According to a list of the world’s “fattest countries” published on Forbes, Pakistan is ranked 165 (out of 194 countries) in terms of its overweight population, with 22.2% of individuals over the age of 15 crossing the threshold of obesity.
Body mass index (BMI) is a measure used to determine childhood overweight and obesity. Overweight is defined as a BMI at or above the 85th percentile and below the 95th percentile for children and teens of the same age and sex. Obesity is defined as a BMI at or above the 95th percentile for children and teens of the same age and sex.
BMI is calculated by dividing a person’s weight in kilograms by the square of height in meters. For children and teens, BMI is age- and sex-specific and is often referred to as BMI-for-age. A child’s weight status is determined using an age- and sex-specific percentile for BMI rather than the BMI categories used for adults. This is because children’s body composition varies as they age and varies between boys and girls. Therefore, BMI levels among children and teens need to be expressed relative to other children of the same age and sex.
For example, a 10-year-old boy of average height (56 inches) who weighs 102 pounds would have a BMI of 22.9 kg/m2. This would place the boy in the 95th percentile for BMI, and he would be considered as obese. This means that the child’s BMI is greater than the BMI of 95% of 10-year-old boys in the reference population.
The CDC Growth Charts are the most commonly used indicator to measure the size and growth patterns of children and teens in the United States.
BMI-for-age weight status categories and the corresponding percentiles were based on expert committee recommendations and are shown in the following table.
| BMI-for-age weight status categories and the corresponding percentiles | |
| Weight Status Category | Percentile Range |
| Underweight | Less than the 5th percentile |
| Normal or Healthy Weight | 5th percentile to less than the 85th percentile |
| Overweight | 85th to less than the 95th percentile |
| Obese | 95th percentile or greater |
BMI does not measure body fat directly, but research has shown that BMI is correlated with more direct measures of body fat, such as skinfold thickness measurements, bioelectrical impedance, densitometry (underwater weighing), dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) and other methods 1,2,3. BMI can be considered an alternative to direct measures of body fat. A trained healthcare provider should perform appropriate health assessments in order to evaluate an individual’s health status and risks.
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a person’s weight in kilograms divided by the square of height in meters. A high BMI can be an indicator of high body fatness.
To calculate BMI, see the Adult BMI Calculator or determine BMI by finding your height and weight in this BMI Index Chart
Obesity is frequently subdivided into categories:
Note: At an individual level, BMI can be used as a screening tool but is not diagnostic of the body fatness or the health of an individual. A trained healthcare provider should perform appropriate health assessments in order to evaluate an individual’s health status and risks. If you have questions about your BMI, talk with your health care provider.
See the following table for an example.
| Height | Weight Range | BMI | Considered |
| 5′ 9″ | 124 lbs or less | Below 18.5 | Underweight |
| 125 lbs to 168 lbs | 18.5 to 24.9 | Healthy weight | |
| 169 lbs to 202 lbs | 25.0 to 29.9 | Overweight | |
| 203 lbs or more | 30 or higher | Obese | |
| 271 lbs or more | 40 or higher | Class 3 Obese |
There is no single or simple solution to the obesity epidemic. It’s a complex problem and there has to be a multifaceted approach. Policy makers, state and local organizations, business and community leaders, school, childcare and healthcare professionals, and individuals must work together to create an environment that supports a healthy lifestyle. There are several ways state and local organizations can create a supportive environment to promote healthy living behaviors that prevent obesity.
The evidence is clear—physical activity fosters normal growth and development, can reduce the risk of various chronic diseases, and can make people feel better, function better, and sleep better. Some health benefits start immediately after activity, and even short bouts of physical activity are beneficial.
Preschool Children Preschool-aged children (ages 3 through 5 years) should be physically active throughout the day to enhance growth and development.
Adult caregivers of preschool-aged children should encourage active play that includes a variety of activity types.
It is important to provide young people opportunities and encouragement to participate in physical activities that are appropriate for their age, that are enjoyable, and that offer variety.
Adults should move more and sit less throughout the day. Some physical activity is better than none. Adults who sit less and do any amount of moderate-to-vigorous physical activity gain some health benefits.
Osteoporosis, which literally means porous bone, is a disease in which the density and quality of bone are reduced. As bones become more porous and fragile, the risk of fracture is greatly increased. The loss of bone occurs silently and progressively.
There typically are no symptoms in the early stages of bone loss. But once your bones have been weakened by osteoporosis, you may have signs and symptoms that include: Back pain, caused by a fractured or collapsed vertebra. Loss of height over time.
The body constantly absorbs and replaces bone tissue. With osteoporosis, new bone creation doesn’t keep up with old bone removal.
Treatment includes medications, healthy diet, and weight-bearing exercise to help prevent bone loss or strengthen already weak bones.
Common medications used for osteoporosis treatment
Good sources of calcium include
Although osteoporosis can strike at any age, it is most common among older people, especially older women. Men also have this disease. White and Asian women are most likely to have osteoporosis, by age 65, men and women are losing bone at the same rate.
Other women at great risk include those who:
Many chronic diseases have genetic components which increases disease risk in certain people. Environment and exposure to polluted air, lifestyle choices including diet and smoking may affect the outcome of chronic disease.